Sun Damage (Photoaging and Skin Cancer)
Sun damage causes premature skin aging and skin cancer. Photoaging is the medical term for premature skin changes that result from cumulative sun damage due to repeated exposure to UV light from the sun. Photoaging affects all areas of your skin that are subjected to repeated intense sun exposure including your face and hands; and makes you look older than your age.
Sunlight contains two types of ultraviolet light, UVA and UVB rays. Photoaging accelerates chronological aging and is responsible for many of the skin changes attributed to aging. UV light from the sun is responsible for 90% of visible is skin changes or skin damage, also called sun damage.
UV light damages the DNA in skin cells and stimulates production of melanin to protect the skin which results in a tan. UVA rays are responsible for photoaging. They degrade collagen and elastin which results in wrinkles and thick, tough skin.
Unavoidable skin changes caused by sun damage include:
- Deterioration of elastin, the substance that gives the skin its flexibility; and collagen, the skin’s structural support.
- Loose skin
- Wrinkles and fine lines
- Rough, leathery skin
- Uneven skin tone
- Dullness
- Broken and dilated blood vessels
- Dryness
- Pigment changes, freckles, brown spots, age spots
- Melasma
- Actinic Keratoses
Sunlight and Vitamin D
Some sun exposure is essential to your health. The skin uses the sun’s UVB rays to produce Vitamin D which is vital for healthy bones and plays other important roles in the body, such as reducing inflammation. We get all the UVB radiation we need to synthesize Vitamin D safely with short exposure – 20 to 30 minutes of midday sun a few times a week. 1 However, it is important to note that excessive exposure to UVB rays can cause skin cancer, which is why Dr. Farhang advises that her patients wear sunscreen.
Sun tanning and Sunburns
Cells called melanocytes in the outermost layer of skin, the epidermis, produce melanin, the pigment that gives the skin its color; and protects the skin from UV radiation. When the skin is exposed to the sun’s UV rays, it produces more melanin, which creates a tan. However, when the skin is exposed to too much UV radiation the result is a sunburn. A sunburn is an inflammatory reaction to UV radiation.
Sunburns accelerate skin aging and are the main cause of all three types of skin cancer – basal cell carcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma and melanoma. Just one blistering sunburn in childhood or adolescence more than doubles your risk of developing skin cancer, including melanoma, the deadliest type of skin cancer. However, too much intense sun exposure even without a sunburn increases your risk for skin cancer because of the damage to the skin’s DNA.
Actinic Keratoses
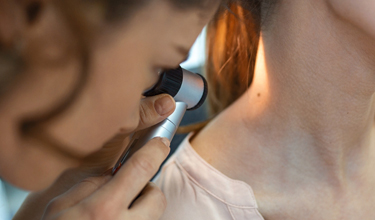
As sun damage accumulates precancerous lesions called actinic keratoses (AKs) can develop. AKs are small, red, rough and scaly patches of skin that may be precancerous. They are usually found on the face, scalp, back of the hands, chest and areas frequently exposed to the sun.
Over time AKs can become squamous cell skin cancer. This is one reason why an annual full body skin check by Dr. Farhang is so important. When discovered early, AKs can be safely removed.
Skin Cancer
Frequent and prolonged exposure to UV radiation from the sun over years is the primary cause of skin cancer.
There are many noninvasive and minimally invasive treatments to reduce the signs of photoaging. Sun protection is vital to protect you from the harmful effects of the sun. Sometimes you can prevent, slow or reverse some of the signs of sun damage. People who live in Tucson (Oro Valley) are fortunate to have easy access to Dr. Sheila Farhang, a board – certified dermatologist and dual accredited fellowship surgeon in Mohs surgery and cosmetic surgery.
Contact Dr. Sheila Farhang at Avant Dermatology and Aesthetics to schedule a consultation and discover how you can turn back the clock and protect yourself from the signs of premature aging.





 / 291 Reviews
/ 291 Reviews
socialize with avant
#naturalskin